Patient Education
Cancer Type
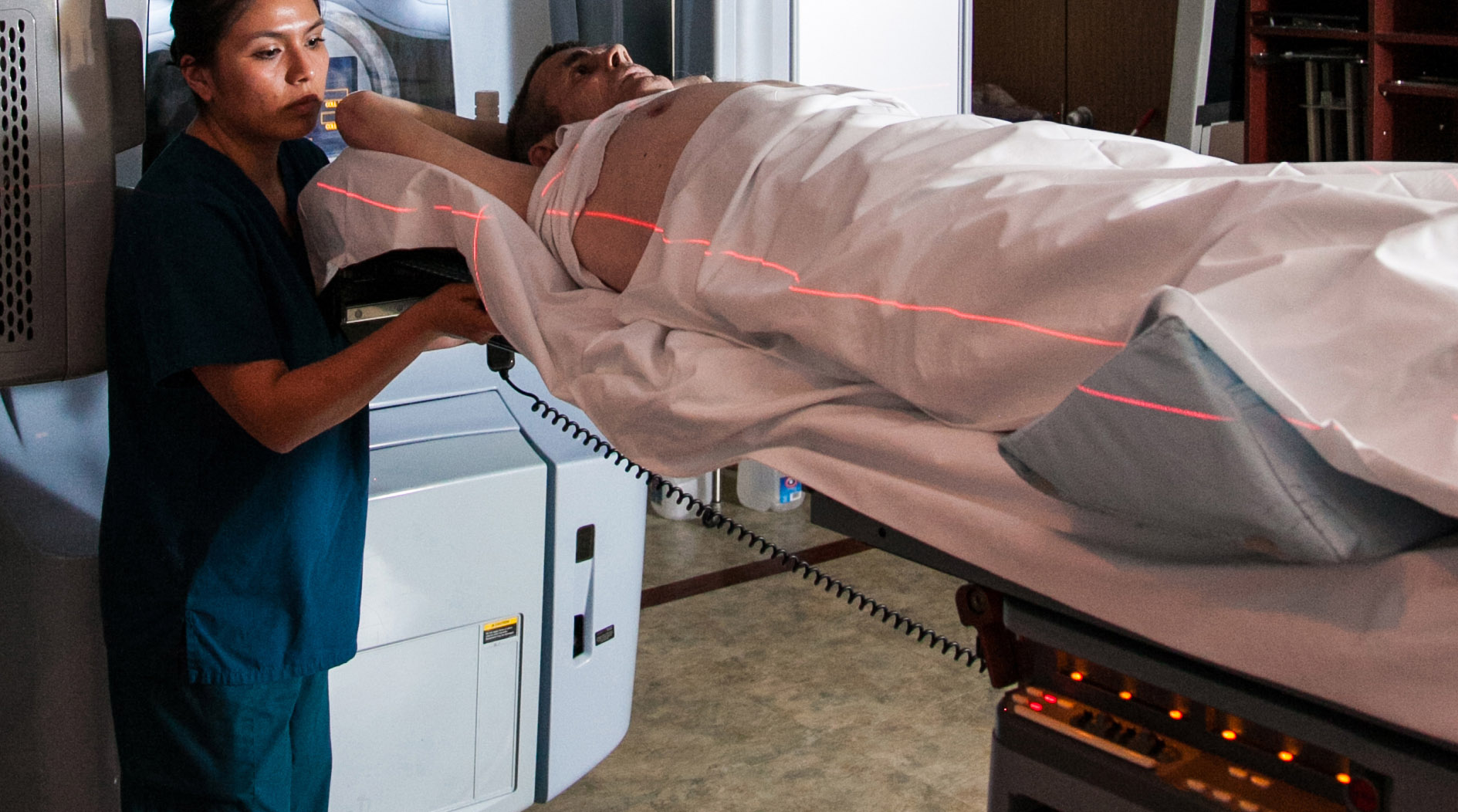
What is Radiation Therapy
Treatment Types
x
The lymphatic system is a network of tiny vessels extending throughout the body. Scattered along these vessels are lymph nodes, which are often adjacent to arteries and veins. The lymphatic vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph from the extremities and organs back to the heart for circulation. The primary job of the lymphatic system is to fight infection and disease. A tumor of the lymphatic system is called lymphoma.
There are two main types of lymphoma: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. They are further classified into subtypes.
Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Hodgkin lymphoma accounts for 10% of all lymphomas diagnosed in the United States, with the majority presenting in two age groups: 15-30 years of age and then another in adults 55 years or older
- An estimated 8,570 people will be diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma in the United States this year
- Hodgkin lymphoma is now curable in at least 80% of patients.
- Depending on the stage, the primary treatment approach for this lymphoma is typically a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a broad term that encompasses a diverse group of lymphomas that differ from Hodgkin lymphoma. The most common subtypes diagnosed in the United States include: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL), follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma.
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma occurs in individuals at almost all ages, but it is uncommon in children.
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is nine times more common than Hodgkin lymphoma, with an estimated 80,620 people diagnosed in the United States this year.
- All types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma are treatable, and many are curable. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is typically treated with chemotherapy, biologic therapy and/or radiation therapy. In some types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, a stem cell transplant may be part of treatment. Depending on your subtype and overall health, you might receive only one of these treatments or you might receive several in combination.
SEARCH RTANSWERS
Doctor Search
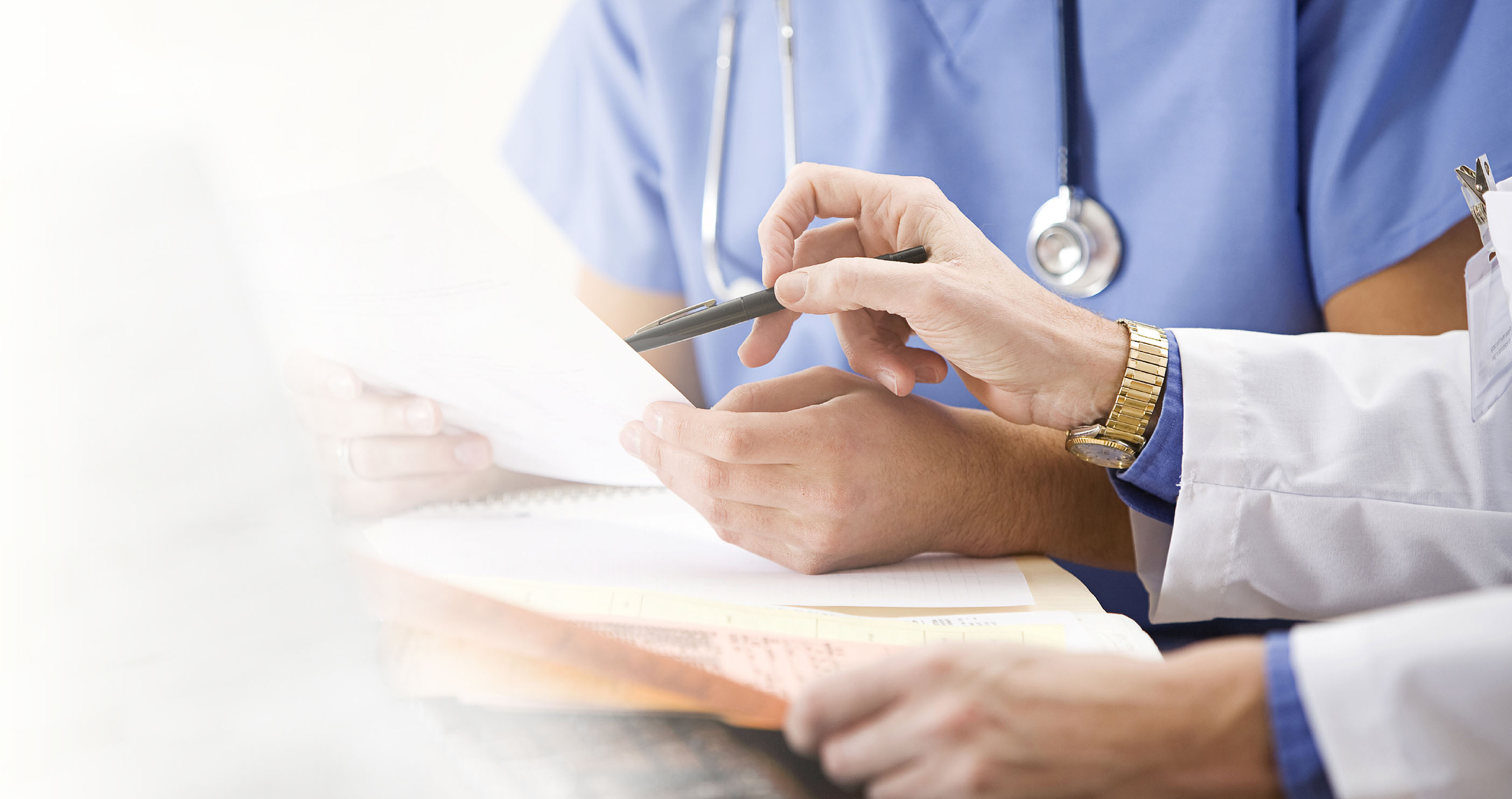

WHAT TO EXPECT
Once a cancer diagnosis is made, you will likely talk with your primary care physician along with several cancer specialists to discuss what happens before, during and after treatment.
CLINICAL TRIALS

Cancer specialists regularly conduct studies to test new treatments. These studies are called clinical trials. Clinical trials are available through cancer doctors everywhere — not just in major cities, university centers or in large hospitals.
SIDE EFFECTS

SIDE EFFECTS
Most of the side effects of radiation therapy are limited to the area being treated. Short-term side effects are related to injury to normal rapidly dividing cells. They are usually temporary, mild and treatable.
TREATMENT TEAM

TREATMENT TEAM
While you undergo radiation therapy, a team of highly trained medical professionals will be working together to make sure you receive the best possible care.